ARC: A Tool to Rate AI Models for Robustness Through a Causal Lens for Enabling Trustworthy Model Selection | ACM Web Conference 2026 Trusted AI
AI models are widely used in web applications and data-driven services that rely on continuously collected and evolving online data. Their decisions can be affected by bias, noise, and shifts in the underlying data. This paper presents ARC, an interactive web-based tool for rating AI models for robustness using causality-based methods. ARC quantifies robustness, encompassing fairness and stability, through causal metrics that measure how predictions vary with perturbations and protected attributes, and allows users to explore trade-offs between robustness and accuracy.
[Demo Video] [Tool]OMEGA: An Ontology-Driven Tool for Explaining Multi-Agent Path Finding | AAAI 2026 Demo Automated Planning Ontology
OMEGA links MAPF execution traces to a planning ontology to produce transparent, queryable explanations of agent actions, conflicts, and resolutions—supporting SPARQL-based “why/why not” queries and traceability across plans and runs.
[Paper] [Demo Video]GAICo: GenAI Results Comparator | IAAI/AAAI 2026 LLM Evaluation Trust Rating
A Python library providing multi-modal evaluation metrics to compare generative AI outputs, often against references. Features streamlined workflows for model comparison and visualization.
[Demo Video] [Repository] [IAAI/AAAI 2026 Paper]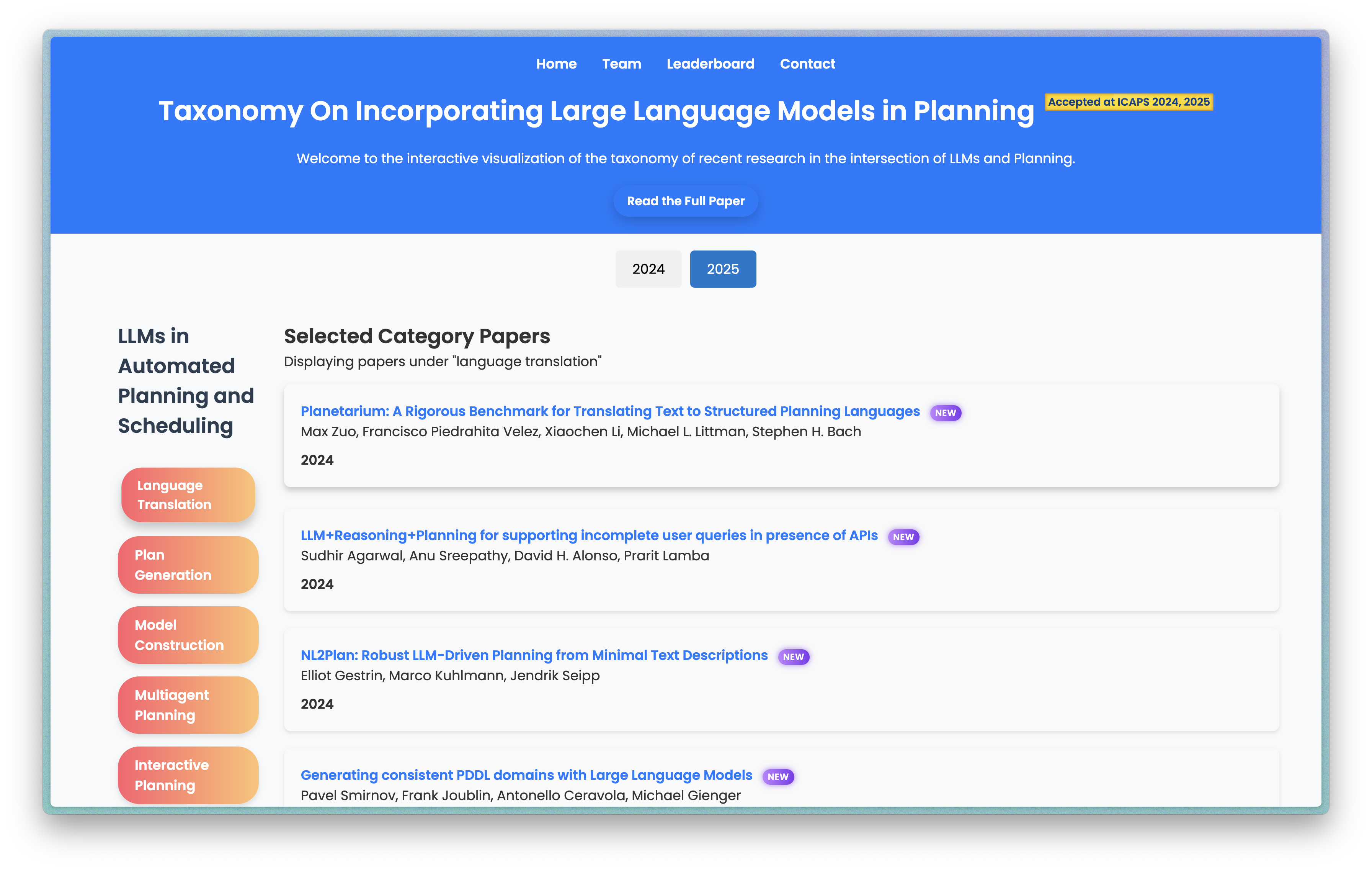
LLM Planning Visualization | 2024 & 2025 Automated Planning LLMs
An interactive tool to centralize and categorize the exponentially growing literature on LLMs and Automated Planning.
[Demo] [ICAPS 2024 Paper] [ICAPS 2025 Paper]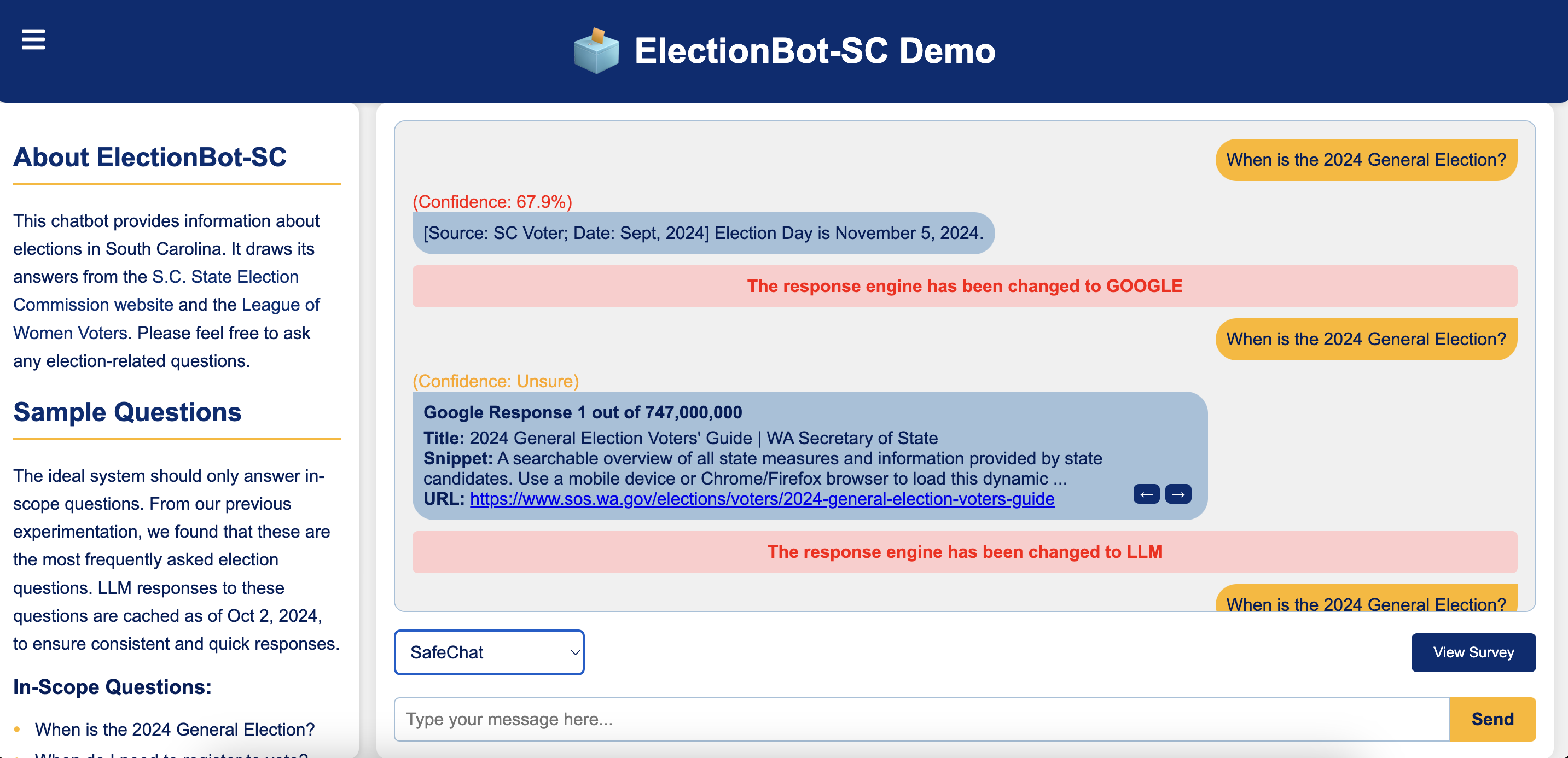
ElectionBot-SC: A Tool to Understand and Compare Chatbot Behavior for Safe Election Information in South Carolina | 2024 Chatbots
We present ElectionBot-SC, a tool designed to provide reliable and accessible election information, featuring three response engines: SafeChat (explained below), Google Search, and a free-tier Large Language Model (LLM): Mixtral 8x7b.
[Paper] [Demo Video]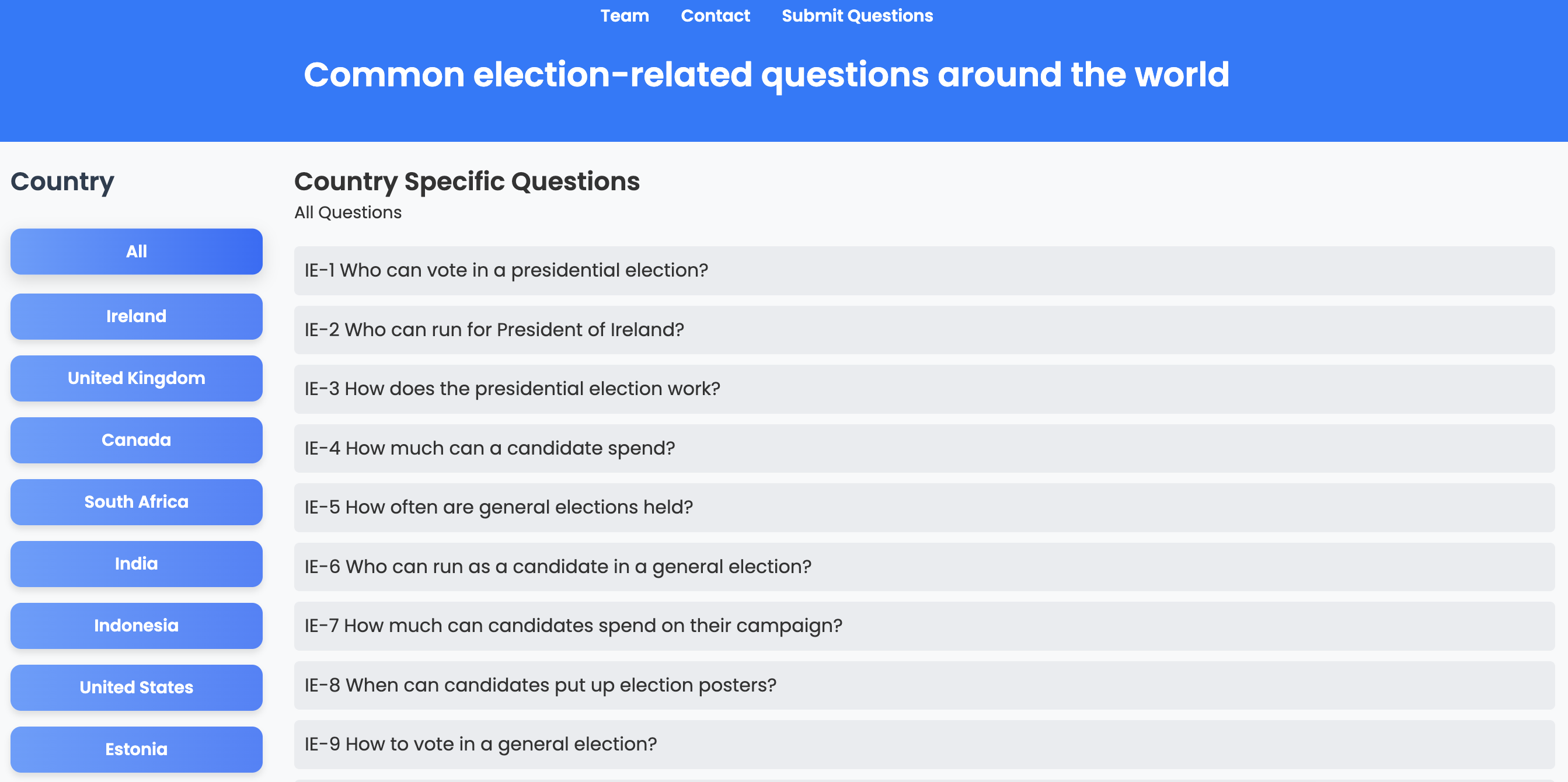
Election-related Questions Around the World | 2024
This website organizes election-related questions by country, highlighting diverse geopolitical contexts and allowing users to submit questions specific to their nation.
[Webpage]
Traffic Data Analysis | 2024
We analyze traffic accidents over time and across various regions, focusing on economic impact, road conditions, and incident hotspots. The insights provided help in understanding patterns and mitigating future risks.
[Demo] [More Details]Solving the Rubik's Cube with a PDDL Planner | ICAPS 2024Neural-Symbolic AI
In this demonstration, we introduce the first PDDL formulation for the 3-dimension RC and solve it with an off-the-shelf Fast-Downward planner. We also create a plan executor and visualizer to show how the plan achieves the intended goal.
[Paper] [More Details]Expressive and Flexible Simulation of Information Spread Strategies in Social Networks Using Planning | AAAI 2024 Automated Planning Best Demo at AAAI-24
We present a demonstration of integrating Automated Planning with opinion dynamics, enabling users to visualize, simulate, and strategically influence opinion evolution in networks. This approach offers a practical solution for understanding and guiding information spread.
[Paper] [Demo Video]ULTRA: A University-Lead Team Builder from RFPs and Analysis | 2024 Recommender Systems
January 2024: Proceedings of the 7th Joint International Conference on Data Science & Management of Data (11th ACM IKDD CODS and 29th COMAD).We introduce ULTRA, a novel AI-based system for assisting team formation when researchers respond to calls for proposals from funding agencies.
[Paper] [Demo Video] [Tool] [BibTex] [More Details]Plansformer Tool: Demonstrating Generation of Symbolic Plans using Transformers | IJCAI 2023Automated Planning
We introduce Plansformer; an LLM fine-tuned on planning problems and capable of generating plans with favorable behavior in terms of correctness and length with reduced knowledge-engineering efforts.
[Paper] [BibTex] [More Details]
ElectionBot for South Carolina | AI Magazine 2023 Chatbots
Here, we demonstrate how a chatbot built with the SafeChat architecture and using official FAQs (questions and their answers) from South Carolina will answer to any user question. The chatbot should only answer when it is confident of the question. The chatbot can make answers consumable but will not cook up (hallucinate) new answers.
[Paper] [Tool] [BibTex]
ElectionBot for Mississippi | AI Magazine 2023 Chatbots
Here, we demonstrate how a chatbot built with the SafeChat architecture and using official FAQs (questions and their answers) from Mississippi will answer to any user question. The chatbot should only answer when it is confident of the question. The chatbot can make answers consumable but will not cook up (hallucinate) new answers.
[Paper] [Tool] [BibTex]ALLURE: A Multi-modal Guided Environment for Helping Children Learn to Solve a Rubik’s Cube | AAAI 2022 Neuro-Symbolic AI
We demonstrate ALLURE, an educational AI system for learning to solve the Rubik’s cube that is designed to help students improve their problem solving skills.
[Paper] [Demo Video] [BibTex] [More Details]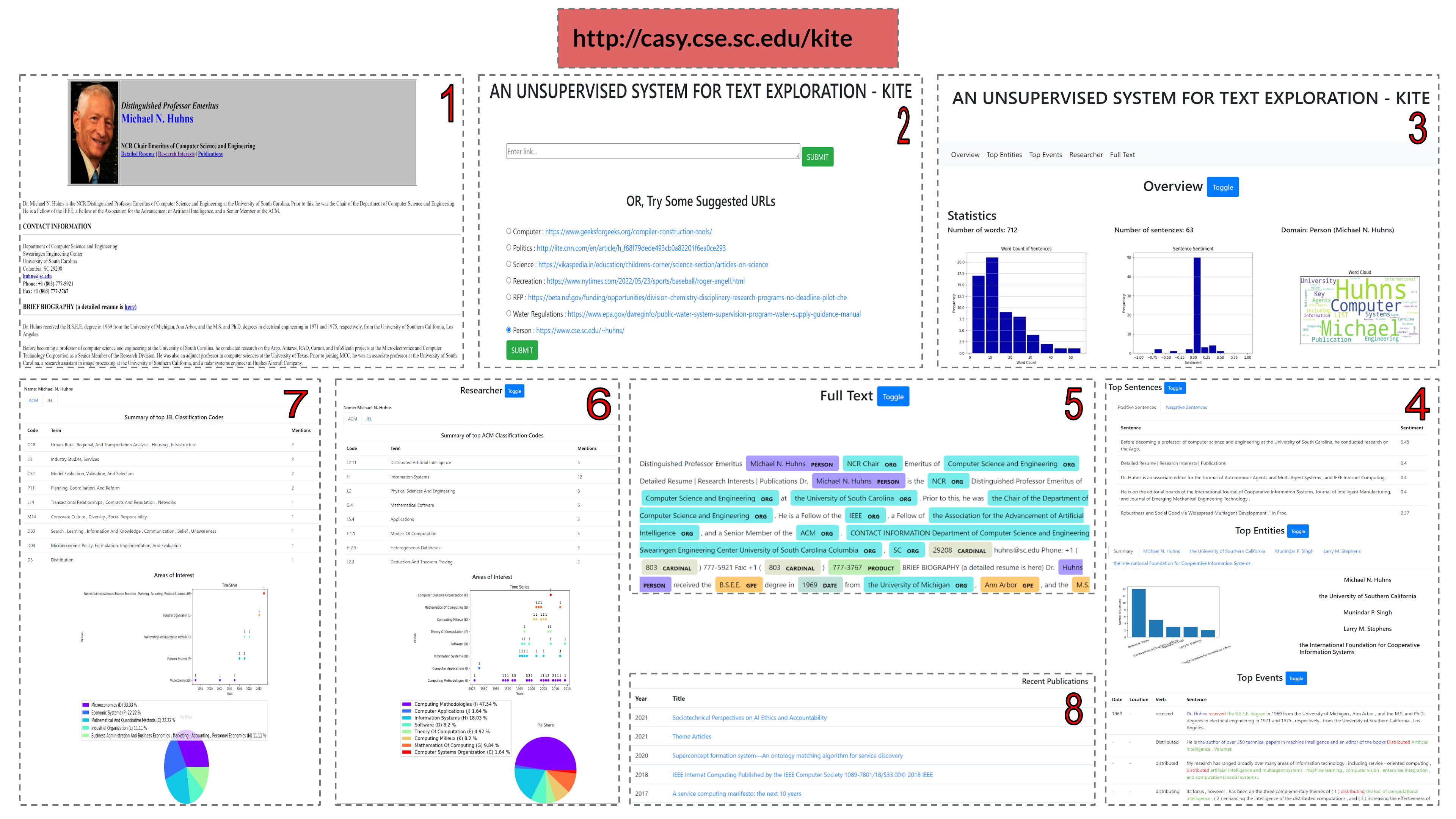
KITE: An Unsupervised, Effective and Inclusive Approach for Textual Content Exploration | 2022 Data Analysis
We present an unsupervised system, called KITE, for exploring textual data which can generate insights from a general as well as domaindependent perspective consisting of holistic views, entity-centric view, events view, domain-specific interpretation using industry taxonomies and a detailed full-text view transparently connecting the document to insight elements.
[Paper] [Demo Video] [Tool] [BibTex]
ROSE: Tool and Data ResOurces to Explore the Instability of SEntiment Analysis Systems | 2022 Data Analysis
Sentiment Analysis Systems (SASs) are data-driven Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems that assign a score conveying the sentiment and emotion intensity when a piece of text is given as input. Like other AI, and especially machine learning (ML) based systems, they have also exhibited instability in their values when inputs are perturbed with respect to gender and race, which can be interpreted as biased behavior. In this demonstration paper, we present ROSE, a resource for understanding the behavior of SAS systems with respect to gender. It consists of data consisting of input text and output sentiment scores and a visualization tool to explore the behavior of SAS. We calculated the output sentiment scores using off-the-shelf SASs and our deep-learning-based implementations based on published architectures.
[Paper] [Demo Video] [Tool] [BibTex]PRUDENT: A Generic Dialog Agent for Information Retrieval Based on Automated Planning Within a Reinforcement Learning Platform | ICAPS 2021Automated Planning
We present a generic approach for dialogs for information retrieval based on automated planning within a reinforcement learning (RL)-based platform, ParlAI.
[Paper] [Github] [BibTex] [More Details]